Day71 DL Review - Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Primary Goals, Common Tasks, and Deep Learning NLP

Natural Language Processing (NLP) is a branch of artificial intelligence (AI) and linguistics dedicated to helping machines comprehend, interpret, generate, and manage human language. It integrates computational methods with linguistic principles, enabling computers to process and analyze extensive amounts of natural language data, including text and speech.
Primary Goals of NLP
- Understanding Human Language: Machines can comprehend written or spoken language, including grammar, syntax, and semantics.
- Generating Human-Like Language: NLP systems can produce meaningful text or speech outputs that mimic human communication.
- Interpreting Sentiment or Meaning: Machines can extract the meaning, intent, or sentiment from the text (e.g., detecting whether a review is positive or negative).
Common NLP Tasks
- Text Classification:
- Assigning a category or label to a text, such as spam detection or sentiment analysis (e.g., classifying a tweet as positive, neutral, or negative).
- Tokenization:
- Breaking text into smaller units (tokens) such as words, subwords, or sentences.
- Named Entity Recognition (NER):
- Identifying and categorizing entities in text, such as names of people, places, organizations, or dates.
- Machine Translation:
- Automatically translating text from one language to another (e.g., Google Translate).
- Part-of-Speech Tagging (POS):
- Labeling each word in a sentence with its grammatical role (e.g., noun, verb, adjective).
- Speech Recognition:
- Converting spoken language into text, such as dictation systems or voice assistants (e.g., Siri, Google Assistant).
- Text Summarization:
- Generating a shorter, coherent version of a longer text while retaining its key information.
- Question Answering:
- Building systems that can automatically answer questions posed in natural language by extracting relevant information from a dataset or knowledge base.
- Sentiment Analysis:
- Analyzing the emotional tone of a text (positive, negative, neutral), often used in social media monitoring and product reviews.
- Analyzing the emotional tone of a text (positive, negative, neutral), often used in social media monitoring and product reviews.
Source: IBM-Natural Language Processing
Types of NLP Approaches
- Rules-based NLP
The earliest uses of NLP consisted of simple if-then decision trees based on preprogrammed rules. These systems were limited to responding to specific prompts, as seen in the original Moviefone, which utilized very rudimentary natural language generation (NLG). Since rules-based NLP does not incorporate machine learning or AI, its capabilities are limited and not scalable.
- Statistical NLP
Developed later, statistical NLP automatically extracts, classifies, and labels text and voice data elements and then assigns a statistical likelihood to each possible meaning of those elements. This relies on machine learning, enabling a sophisticated breakdown of linguistics, such as part-of-speech tagging. Statistical NLP introduced the essential technique of mapping language elements—words and grammatical rules—to a vector representation so that language can be modeled using mathematical (statistical) methods, including regression or Markov models. This informed early NLP developments such as spellcheckers and T9 texting (Text on nine keys, to be used on Touch-Tone telephones).
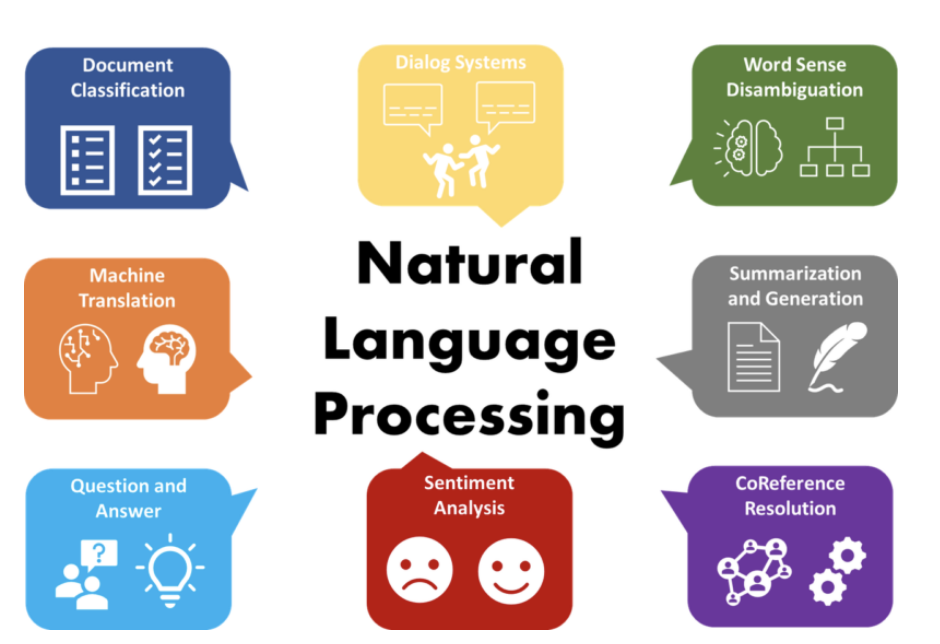
Image Source: GippLab "Deep Learning for Natural Language Processing"
- Deep learning NLP
Deep learning models have recently emerged as the leading approach in NLP, harnessing vast amounts of unstructured data—text and voice—to improve accuracy. Deep learning represents an advanced stage of statistical NLP, distinguished by its reliance on neural network models. Within this domain, several subcategories of models exist:
- Word Embeddings:
- Word embeddings are dense vector representations of words that capture meanings based on context. Deep learning models use these embeddings as word input representations, with popular embedding methods including Word2Vec, GloVe, and FastText.
- Word embeddings map words into a continuous vector space where semantically similar words are placed closer together, capturing word relationships like “king” is to “queen” as “man” is to “woman.”
- Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs):
- RNNs were one of the early deep-learning architectures used in NLP to model data sequences, such as text. They process input tokens sequentially and maintain a hidden state that captures information from previous time steps. Variants like Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) and Gated Recurrent Units (GRUs) help address problems like the vanishing gradient, enabling the capture of longer-range dependencies in text.
- Example task: Text generation, where RNNs can predict the next word in a sequence based on previous words.
- Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) in NLP:
- Although CNNs are more commonly used in image processing, they can also be applied to NLP tasks by treating text as 1D sequences of words or characters. CNNs can capture local patterns (like n-grams) and are often used for sentence classification or semantic similarity detection functions.
- Example task: Sentiment analysis, where CNNs can classify whether a sentence expresses positive or negative sentiment.
- Attention Mechanisms:
- Attention mechanisms allow a model to focus on different parts of an input sequence when making predictions. Rather than relying solely on the hidden state at the final time step (as in RNNs), attention allows the model to “attend” to relevant tokens throughout the sequence.
- Example task: Machine translation, in which attention helps the model focus on specific words in the source sentence while generating each word in the target sentence.
- Transformers:
- Transformers are NLP’s most significant deep learning architecture, introduced in the 2017 paper “Attention is All You Need.” They use self-attention mechanisms to process entire sequences in parallel, allowing them to model long-range dependencies more efficiently than RNNs or CNNs. Since then, transformers have become the foundation of state-of-the-art NLP models.
- Transformers consist of an encoder (for understanding the input) and a decoder (for generating output) and rely on multi-head self-attention to capture relationships between tokens in a sequence.
- Example tasks: Machine translation, summarization, and question answering.
- Pre-trained Language Models:
- Pre-trained models have become the cornerstone of modern NLP. These models are trained on large corpora to learn rich language representations and can be fine-tuned for specific tasks with relatively small datasets. Examples include:
- **BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers) is a transformer-based model trained to predict missing words in a sentence (masked language modeling) and classify sentence pairs. It has performed state-of-the-art tasks such as question answering, named entity recognition, and text classification.
- GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer): GPT is another transformer-based model focusing on autoregressive tasks. The model generates text in these tasks by predicting the next word based on the previous context. GPT-3, in particular, has demonstrated impressive capabilities in generating human-like text.
- T5 (Text-to-Text Transfer Transformer): T5 treats every NLP task as a text-to-text problem, with text as inputs and outputs. This allows it to perform tasks like translation, summarization, and question-answering using a unified framework.
- XLNet, RoBERTa, T5, and DistilBERT are popular pre-trained transformer-based models used in modern NLP.
- Pre-trained models have become the cornerstone of modern NLP. These models are trained on large corpora to learn rich language representations and can be fine-tuned for specific tasks with relatively small datasets. Examples include:
- Transfer Learning:
- Transfer learning in NLP involves fine-tuning pre-trained models (like BERT, GPT, or T5) on specific tasks. These models, trained on large, diverse corpora, can be adapted to various tasks such as sentiment analysis, text classification, and entity recognition with minimal additional training, improving accuracy and reducing the need for large datasets.
- Example task: Fine-tuning BERT for a task like named entity recognition (NER) on a specific dataset.
Leave a comment