Day98 DL Review - Revisiting LLM models (Hand-Written Tree Map)
Language Models- Transfer Learning, Basic Concepts & Terminologies, Components of NLP Models, and Attention Mechanism

I developed a mind map to revisit and review Language Modeling concepts for my upcoming project on the LLM MLops Model. This mind map captures my understanding of foundational and advanced NLP concepts, primarily focusing on model architectures (such as RNNs and transformers), mechanisms (like attention and embeddings), and training methodologies.
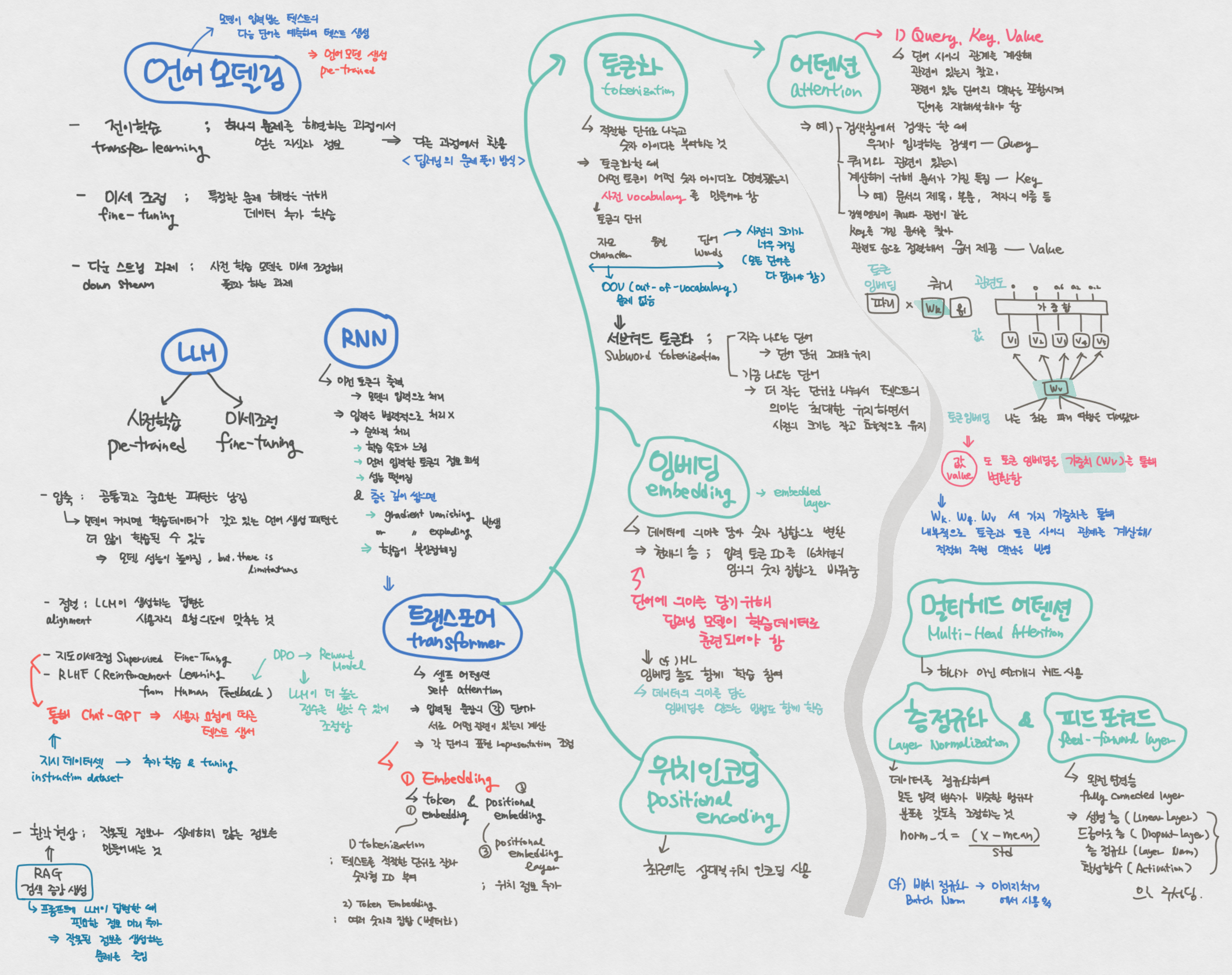
1. Language Modeling
- Transfer Learning: Using a pre-trained model on one task to improve performance on a related task.
- Fine-Tuning: Adapting a pre-trained model by further training on a specific downstream task.
- Downstream Tasks: Tasks that use the output of a pre-trained model, such as classification, translation, or question answering.
- Types of Language Models
- LLM (Large Language Model): Trained on massive datasets, often requiring pre-training and fine-tuning.
- RNN (Recurrent Neural Network): Known for sequential processing but has limitations like vanishing gradients, which affect long-range dependencies.
2. Components of NLP Models
- Tokenization
- Breaking text into units called tokens.
- Methods include word-based, character-based, and subword tokenization.
- Embedding
- Converts tokens into dense vectors to represent meanings and semantic relationships.
- Includes pre-trained and contextual embeddings, where token meaning changes based on context.
- Positional Encoding
- Adds information about the order of tokens in a sequence, which is necessary for transformer models that process input non-sequentially.
3. Attention Mechanism
- Core Components: Query, Key, Value.
- Self-Attention: Each word focuses on other words in the sentence to capture relationships and context.
- Multi-Head Attention
- It uses multiple attention heads to capture different aspects of the input sequence.
- Transformers
- It was built using attention mechanisms, positional encoding, and other layers like normalization and feed-forward layers.
4. Additional Transformer Components
- Layer Normalization
- Normalizes inputs to each layer, helping with model stability and training speed.
- Feed-Forward Layer
- Processes each token independently using linear transformations and activation functions, enhancing the model’s capacity.
5. Advanced Techniques
- Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF)
- They are used in models like ChatGPT, incorporating human feedback for fine-tuning.
- RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation)
- Combines language models with a retrieval system to fetch relevant information, enhancing response accuracy.
- Combines language models with a retrieval system to fetch relevant information, enhancing response accuracy.
Leave a comment